Is there such a thing as a 100% clear balloon?
Have you ever wondered if you could find a balloon that is totally see-through? Does a balloon exist that is completely clear1?
No, a truly 100% clear balloon2 does not exist. The materials used to make balloons, especially natural latex3, have properties that prevent them from being perfectly transparent.
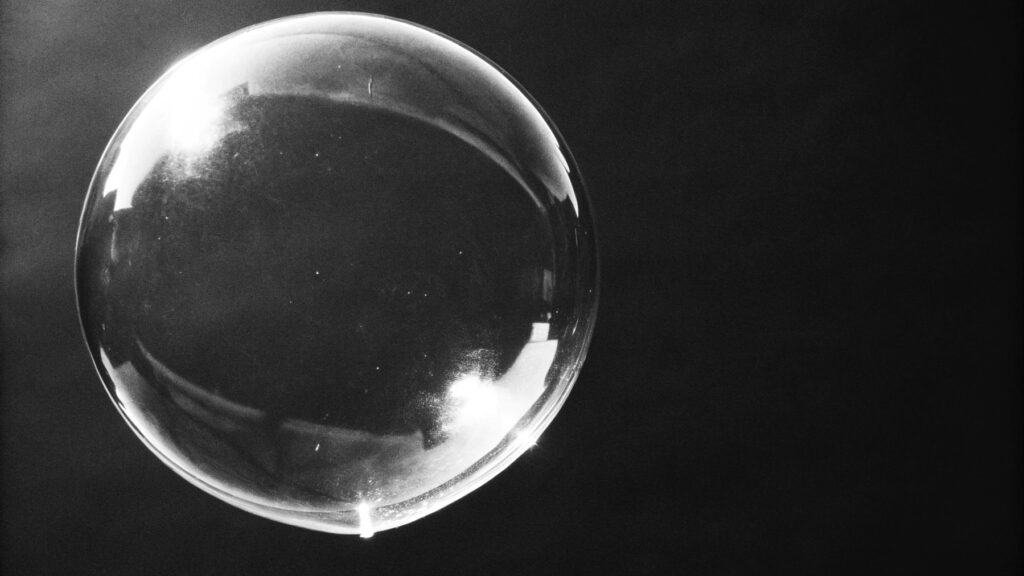

We try very hard at AIHUA BALLOON to make our balloons as clear as possible. We use good, eco-friendly materials4. This helps our balloons look clearer when you inflate them. But there are reasons why a balloon cannot be absolutely 100% clear.
Is it possible to create a balloon that is entirely transparent at a molecular level?
Do you wish you could see right through a balloon, like it wasn't even there? Could we make a balloon where every tiny part is clear?
It is not possible to make a balloon that is 100% transparent at the molecular level5 using current balloon materials. Even the clearest materials have microscopic structures that scatter light6.
Let me tell you why this is. Natural latex, which many balloons are made from, comes from trees. It has proteins and other things in it. These small particles are mixed into the latex. When light hits these particles, it bounces off them. This is called scattering. Scattering makes the material look cloudy or less clear. We clean the latex as much as we can. We remove many of these particles. But some will always be there. Think about water from a river. Even after you filter it, it might still have tiny bits you can't see. This makes it not perfectly clear. The same is true for latex.
Why is it hard to make materials perfectly transparent?
- Light Scattering7: Light is what helps us see. When light goes through something, it can hit small things inside it. These small things make the light go in different directions. This makes the material look less clear.
- Material Structure8: Even clear materials have a structure made of atoms and molecules. These structures can also affect how light moves through them.
- Impurities9: Materials often have small bits of other things inside them. These are called impurities. Impurities can scatter light and make things look less clear.
Comparing Materials for Transparency
| Material Type | Typical Transparency | Reason for Transparency Level |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Latex | Mostly Transparent | Contains proteins and particles that scatter light. |
| PVC (Plastic Film) | Very Transparent | Can be made very smooth and uniform. |
| TPU (Plastic Film) | Very Transparent | Flexible and can be made with few impurities. |
We choose materials that are naturally more transparent. But we can only get them so clear. We can't make the molecules themselves invisible.
What materials would be needed to achieve perfect clarity in a balloon?
Imagine holding a balloon you can barely see, like it's made of air itself. What kind of stuff would we need to make a balloon that clear?
To achieve perfect clarity in a balloon, you would need a material that does not scatter or absorb light at all. Such a material is not currently used for making flexible, stretchable balloon films.

Making something perfectly clear is very difficult. Think about glass. Some glass is very clear, like the glass in a good window. But even the best glass is not 100% clear. It still absorbs a little light. It still has tiny imperfections that can scatter light. For balloons, we need materials that are not hard like glass. We need materials that can stretch a lot. They need to be flexible. Natural latex is very flexible. It can stretch many times its size. Plastic films like PVC and TPU are also flexible, but not as much as latex. These flexible materials10 have structures that prevent perfect clarity. They might have small pockets of air inside them. They might have parts that are not perfectly smooth. These things make light scatter.
Ideal Material Properties for Perfect Clarity
- No Light Absorption: The material should not soak up any light as it passes through.
- No Light Scattering: The material should not make light bounce off in different directions.
- Perfect Uniformity: The material should be exactly the same everywhere, with no differences in its structure.
Challenges with Current Balloon Materials
| Material Type | Flexibility Level | Clarity Level | Challenges for Perfect Clarity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Latex | High | Moderate to High | Natural impurities, molecular structure causes scattering. |
| PVC Film | Medium | High | Can be made very clear, but still has some internal structure. |
| TPU Film | Medium | Very High | Can be made very clear, but manufacturing process can introduce issues. |
Even the clearest plastic films we use, like some types of TPU, are not 100% perfect. They are very clear, yes. But not absolutely, perfectly, totally clear.
How does the refractive index11 of balloon materials affect their transparency?
Have you ever seen a glass of water and noticed how things behind it look bent or distorted? How does this bending of light relate to how clear a balloon is?
The refractive index of a material tells us how much light bends when it passes through that material. Differences in refractive index within a material or between a material and air can cause light to scatter, reducing transparency.
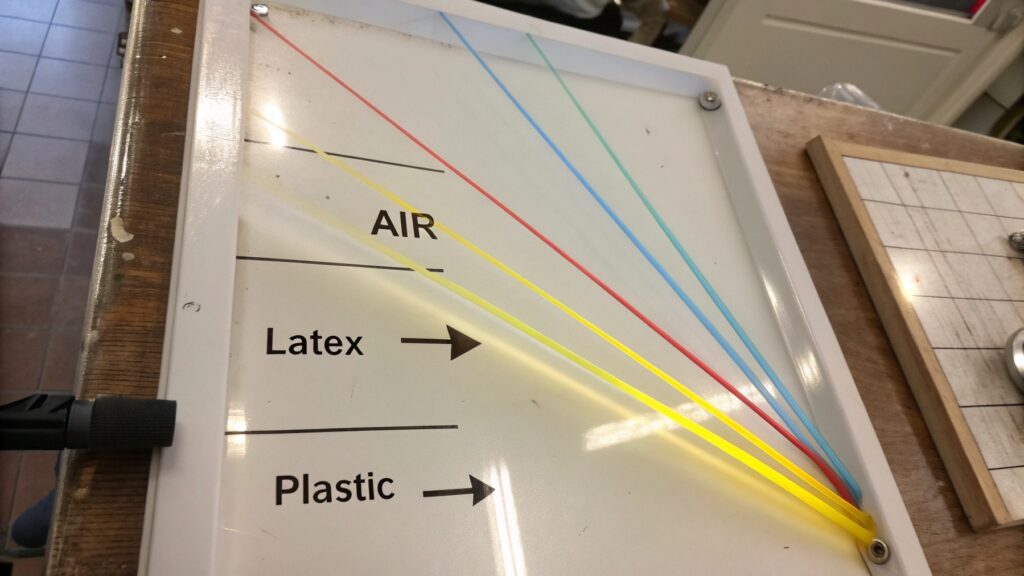

The refractive index is a number. This number shows how much light slows down and bends when it goes from one thing to another. For example, light moves fast in air. It slows down when it enters water or glass. This change in speed makes the light bend. If a material has the same refractive index everywhere inside it, light will go straight through without bending within the material. But if the refractive index changes from one spot to another, the light will bend differently in different spots. This makes the light spread out, which is scattering. Also, when light goes from the air (low refractive index) into the balloon material (higher refractive index), it bends. When it comes back out of the balloon material into the air, it bends again. If the surfaces of the balloon are perfectly smooth and uniform, this bending is predictable and doesn't reduce clarity much. But if the surfaces are not perfectly smooth, or if the material itself has parts with different refractive indexes (like impurities or different structures), then the light will bend and scatter. This makes the balloon look less clear.
Refractive Index and Scattering
- Uniform Material: If the material has the same refractive index throughout, light passes through without internal scattering.
- Varying Refractive Index: If different parts of the material have different refractive indexes (due to impurities, density changes, etc.), light will bend and scatter within the material.
- Surface Effects: Differences in refractive index between the material and the surrounding air, combined with surface roughness, can cause light to reflect and scatter.
Refractive Index of Balloon Materials vs. Air
| Material Type | Typical Refractive Index | Refractive Index of Air | Impact on Clarity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Latex | Around 1.52 | ~1.00 | Significant difference, internal variations scatter. |
| PVC Film | Around 1.53 | ~1.00 | Significant difference, but can be very uniform. |
| TPU Film | Around 1.48 | ~1.00 | Significant difference, can be made very uniform. |
While the materials we use have a higher refractive index than air, which causes some light bending at the surface, the biggest issue for perfect clarity comes from variations in refractive index within the material itself, due to its composition and structure.
Are there any physics limitations preventing a truly 100% clear balloon?
Can the rules of nature, the laws of physics, stop us from ever making a balloon that is completely invisible, completely clear? Are there limits set by science?
Yes, fundamental physics principles related to light interaction with matter place limitations on achieving 100% clarity in any real-world material, including balloon films.

Physics tells us how light behaves when it meets matter. Light is made of photons. When photons hit atoms and molecules in a material, they can be absorbed, transmitted, or scattered. For something to be perfectly clear, all photons must pass straight through without being absorbed or scattered. This is extremely difficult to achieve. Even the clearest known materials, like the glass used in telescopes, absorb a tiny amount of light. They also have tiny imperfections that cause a small amount of scattering. At the atomic level, even perfectly arranged atoms can interact with light in ways that cause a very small amount of scattering. This is related to how electrons in atoms respond to the electric field of light. For flexible materials like those used in balloons, it is even harder to achieve perfect uniformity and avoid all impurities. The very properties that make a material flexible can also make it less perfectly clear. The long chains of molecules in polymers (plastics and latex) can arrange in ways that scatter light. Think about a tangled ball of string versus a single straight string. Light goes through the single string more easily. The structure of balloon materials is more like the tangled string.
Physics Principles Limiting Clarity
- Absorption: Materials absorb light when photons transfer energy to electrons in the material. All real materials absorb some light.
- Rayleigh Scattering: Even in a perfectly uniform material, light can scatter off the density fluctuations that naturally occur due to the movement of atoms and molecules. This type of scattering is more significant for shorter wavelengths of light (like blue light), which is why the sky is blue and distant objects can look hazy.
- Mie Scattering: Scattering caused by particles or imperfections larger than the wavelength of light. Impurities and structural variations in balloon material cause Mie scattering.
- Reflection: Light reflects off surfaces where there is a change in refractive index (like the surface of the balloon). Even smooth surfaces cause some reflection.
Why 100% Clarity is a Theoretical Ideal
| Limitation Factor | Description | Impact on Balloon Clarity |
|---|---|---|
| Light Absorption | Material soaking up light energy. | Reduces the total amount of light passing through. |
| Light Scattering | Light bouncing off particles or structure variations. | Makes the material look cloudy or hazy, distorts the image seen through it. |
| Surface Reflection | Light bouncing off the inner and outer surfaces. | Reduces the amount of light passing through, can cause glare. |
| Material Structure | Non-uniform arrangement of molecules. | Creates internal points of scattering. |
Because of these basic physics principles, achieving absolute 100% clarity where zero light is absorbed, scattered, or reflected is not possible with any known real-world material that can be made into a flexible balloon film. We can get very, very close, but never truly 100%.
Conclusion
So, while we work hard to make our balloons look as clear as possible using good materials, a balloon that is 100% clear, totally invisible, is not possible because of the basic physics of light and the nature of the materials we use.
-
Discover the materials and technologies that influence balloon transparency and their practical applications. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the limitations of balloon materials and the science behind transparency. ↩
-
Learn about natural latex and its properties that impact the clarity of balloons, enhancing your knowledge of balloon manufacturing. ↩
-
Exploring this link will provide insights into sustainable practices in balloon production, enhancing your understanding of eco-friendly options. ↩
-
This resource will delve into the science of transparency in materials, offering a deeper understanding of molecular structures and light scattering. ↩
-
Understanding light scattering can enhance your knowledge of optics and material science, making this link a valuable resource. ↩
-
Understanding light scattering is crucial for grasping why materials can't be perfectly transparent. Explore this link for deeper insights. ↩
-
Material structure plays a key role in transparency. Discover more about its impact on light transmission through this resource. ↩
-
Impurities can significantly affect clarity. Learn more about their role in material transparency by checking this link. ↩
-
Discover the best flexible materials that balance clarity and functionality, essential for various applications including balloons. ↩
-
Understanding the refractive index is crucial for grasping how materials interact with light, impacting their clarity and transparency. ↩
